Python实现的多线程端口扫描工具分享
昨晚今晚写了两晚,总算把Py Port Scanner 写完了,姑且称之为0.1版本,算是一个Python多线程端口扫描工具。
水平有限,实话中间有一些困惑和不解的地方,代码可能也写的比较乱。有些问题并未找到很好的解决方法,还望大家谅解。速度大家自己试验,我感觉还行。
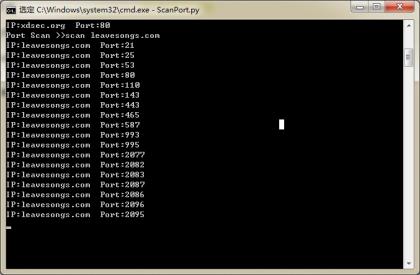
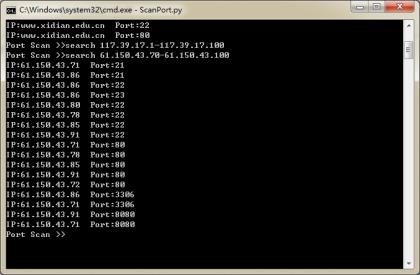
送上效果图两份,分别是扫单IP和扫IP段:
源码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__author__ = 'Phtih0n'
import threading, socket, sys, cmd, os, Queue
#扫描常用端口
PortList = [21, 22, 23, 25, 80, 135, 137, 139, 445, 1433, 1502, 3306, 3389, 8080, 9015]
#得到一个队列
def GetQueue(list):
PortQueue = Queue.Queue(65535)
for p in list:
PortQueue.put(p)
return PortQueue
#单IP扫描线程个数
nThread = 20
#线程锁
lock = threading.Lock()
#超时时间
Timeout = 3.0
#打开的端口列表
OpenPort = []
class ScanThread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, scanIP):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.IP = scanIP
def Ping(self, Port):
global OpenPort, lock, Timeout
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
sock.settimeout(Timeout)
address = (self.IP, Port)
try:
sock.connect(address)
except:
sock.close()
return False
sock.close()
OpenPort.append(Port)
if lock.acquire():
print "IP:%s Port:%d" % (self.IP, Port)
lock.release()
return True
class ScanThreadSingle(ScanThread):
def __init__(self, scanIP, SingleQueue):
ScanThread.__init__(self, scanIP)
self.SingleQueue = SingleQueue
def run(self):
while not self.SingleQueue.empty():
p = self.SingleQueue.get()
self.Ping(p)
class ScanThreadMulti(ScanThread):
def __init__(self, scanIP, PortList):
ScanThread.__init__(self, scanIP)
self.List = PortList[:]
def run(self):
for p in self.List:
self.Ping(p)
class Shell(cmd.Cmd):
u'''Py Port Scanner 0.1 使用说明:
port [port..] 设置扫描的端口,用逗号分隔。
默认:21, 22, 23, 25, 80, 135, 137, 139, 445, 1433, 1502, 3306, 3389, 8080, 9015
example:port 21,23,25
example: port 1000..2000
example: port 80,443,1000..1500
scan [IP] 扫描某一IP地址
example: scan 192.168.1.5
search [IP begin]-[IP end] 扫描某一IP段
example: search 192.168.1.1-192.168.1.100
time [timeout] 设置超时时间,默认为3秒
example: time 5
cls 清楚屏幕内容
listport 打印端口列表
help 打开本帮助
'''
def __init__(self):
cmd.Cmd.__init__(self)
reload(sys)
sys.setdefaultencoding('utf-8')
self.prompt = "Port Scan >>"
self.intro = "Py Port Scanner 0.1"
def do_EOF(self, line):
return True
def do_help(self, line):
print self.__doc__
#设置端口
def do_port(self, line):
global PortList
PortList = []
ListTmp = line.split(',')
for port in ListTmp:
if port.find("..") < 0:
if not port.isdigit():
print "输入错误"
return False
PortList.append(int(port))
else:
RangeLst = port.split("..")
if not (RangeLst[0].isdigit() and RangeLst[1].isdigit()):
raise ValueError
exit()
for i in range(int(RangeLst[0]), int(RangeLst[1])):
PortList.append(i)
def do_scan(self, line):
global nThread, PortList
ThreadList = []
strIP = line
SingleQueue = GetQueue(PortList)
for i in range(0, nThread):
t = ScanThreadSingle(strIP, SingleQueue)
ThreadList.append(t)
for t in ThreadList:
t.start()
for t in ThreadList:
t.join()
def do_search(self, line):
global nThread, PortList
ThreadList = []
(BeginIP, EndIP) = line.split("-")
try:
socket.inet_aton(BeginIP)
socket.inet_aton(EndIP)
except:
print "输入错误"
return
IPRange = BeginIP[0:BeginIP.rfind('.')]
begin = BeginIP[BeginIP.rfind('.') + 1:]
end = EndIP[EndIP.rfind('.') + 1:]
for i in range(int(begin), int(end)):
strIP = "%s.%s" % (IPRange, i)
t = ScanThreadMulti(strIP, PortList)
ThreadList.append(t)
for t in ThreadList:
t.start()
for t in ThreadList:
t.join()
def do_listport(self, line):
global PortList
for p in PortList:
print p,
print '\n'
def do_time(self, line):
global Timeout
try:
Timeout = float(line)
except:
print u"参数错误"
def do_cls(self, line):
os.system("cls")
if '__main__' == __name__:
try:
os.system("cls")
shell = Shell()
shell.cmdloop()
except:
exit()