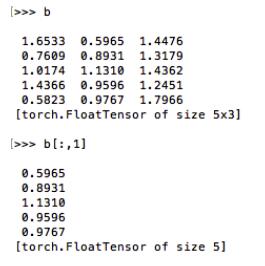
实例讲解Python中函数的调用与定义
调用函数:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# 函数调用
>>> abs(100)
100
>>> abs(-110)
110
>>> abs(12.34)
12.34
>>> abs(1, 2)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: abs() takes exactly one argument (2 given)
>>> abs('a')
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: bad operand type for abs(): 'str'
>>> max(1, 2)
2
>>> max(2, 3, 1, -5)
3
>>> int('123')
123
>>> int(12.34)
12
>>> str(1.23)
'1.23'
>>> str(100)
'100'
>>> bool(1)
True
>>> bool('')
False
>>> a = abs # 变量a指向abs函数,相当于引用
>>> a(-1) # 所以也可以通过a调用abs函数
1
>>> n1 = 255
>>> n2 = 1000
>>> print(hex(n1))
0xff
>>> print(hex(n2))
0x3e8
定义函数:
#!/usr/bin/env python3 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- #函数定义 def myAbs(x): if x >= 0: return x else: return -x a = 10 myAbs(a) def nop(): # 空函数 pass
pass语句什么都不做 。
实际上pass可以用来作为占位符,比如现在还没想好怎么写函数代码,就可以先写一个pass,让代码运行起来。
if age >= 18:
pass
#缺少了pass,代码就会有语法错误
>>> if age >= 18:
...
File "<stdin>", line 2
^
IndentationError: expected an indented block
>>> myAbs(1, 2)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: myAbs() takes 1 positional argument but 2 were given
>>> myAbs('A')
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "<stdin>", line 2, in myAbs
TypeError: unorderable types: str() >= int()
>>> abs('A')
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: bad operand type for abs(): 'str'
def myAbs(x):
if not isinstance(x, (int, float)):
raise TypeError('bad operand type')
if x >= 0:
return x
else:
return -x
>>> myAbs('A')
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "<stdin>", line 3, in myAbs
TypeError: bad operand type
返回两个值?
import math def move(x, y, step, angle = 0): nx = x + step * math.cos(angle) ny = y - step * math.sin(angle) return nx, ny >>> x, y = move(100, 100, 60, math.pi / 6) >>> print(x, y) 151.96152422706632 70.0
其实上面只是一种假象,Python函数返回的仍然是单一值 。
>>> r = move(100, 100, 60, math.pi / 6) >>> print(r) (151.96152422706632, 70.0)
实际上返回的是一个tuple!
但是,语法上,返回一个tuple可以省略括号, 而多个变量可以同时接受一个tuple,按位置赋给对应的值。
所以,Python的函数返回多值实际就是返回一个tuple,但是写起来更方便。
函数执行完毕也没有return语句时,自动return None。
练习 :
import math def quadratic(a, b, c): x1 = (-b + math.sqrt(b * b - 4 * a * c)) / (2 * a) x2 = (-b - math.sqrt(b * b - 4 * a * c)) / (2 * a) return x1, x2 x1, x2 = quadratic(2, 5, 1) print(x1, x2) >>> import math >>> def quadratic(a, b, c): ... x1 = (-b + math.sqrt(b * b - 4 * a * c)) / (2 * a) ... x2 = (-b - math.sqrt(b * b - 4 * a * c)) / (2 * a) ... return x1, x2 ... >>> x1, x2 = quadratic(2, 5, 1) >>> print(x1, x2) -0.21922359359558485 -2.2807764064044154