python单线程文件传输的实例(C/S)
客户端代码:
#-*-encoding:utf-8-*-
import socket
import os
import sys
import math
import time
def progressbar(cur, total):
percent = '{:.2%}'.format(float(cur) / float(total))
sys.stdout.write('\r')
sys.stdout.write("[%-50s] %s" % (
'=' * int(math.floor(cur * 50 / total)),
percent))
sys.stdout.flush()
def getFileSize(file):
file.seek(0, os.SEEK_END)
fileLength = file.tell()
file.seek(0, 0)
return fileLength
def getFileName(fileFullPath):
index = fileFullPath.rindex('\\')
if index == -1:
return fileFullPath
else:
return fileFullPath[index+1:]
def transferFile():
fileFullPath = r"%s" % raw_input("File path: ").strip("\"")
if os.path.exists(fileFullPath):
timeStart = time.clock()
file = open(fileFullPath, 'rb')
fileSize = getFileSize(file)
client = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
client.connect((targetHost, targetPort))
# send file size
client.send(str(fileSize))
response = client.recv(1024)
# send file name
client.send(getFileName(fileFullPath))
response = client.recv(1024)
# send file content
sentLength = 0
while sentLength < fileSize:
bufLen = 1024
buf = file.read(bufLen)
client.send(buf)
sentLength += len(buf)
process = int(float(sentLength) / float(fileSize) * 100)
progressbar(process, 100)
client.recv(1024)
file.close()
timeEnd = time.clock()
print "\r\nFinished, spent %d seconds" % (timeEnd - timeStart)
else:
print "File doesn't exist"
targetHost = raw_input("Server IP Address: ")
targetPort = int(raw_input("Server port: "))
while True:
transferFile()
服务器端代码:
#-*-encoding:utf-8-*-
import socket
import threading
import os
import sys
import math
bindIp = "0.0.0.0"
bindPort = 9999
server = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
server.bind((bindIp, bindPort))
server.listen(1)
print "Listening on %s:%d" % (bindIp, bindPort)
def progressbar(cur, total):
percent = '{:.2%}'.format(float(cur) / float(total))
sys.stdout.write('\r')
sys.stdout.write("[%-50s] %s" % (
'=' * int(math.floor(cur * 50 / total)),
percent))
sys.stdout.flush()
def checkFileName(originalFileName):
extensionIndex = originalFileName.rindex(".")
name = originalFileName[:extensionIndex]
extension = originalFileName[extensionIndex+1:]
index = 1
newNameSuffix = "(" + str(index) + ")"
finalFileName = originalFileName
if os.path.exists(finalFileName):
finalFileName = name + " " + newNameSuffix + "." + extension
while os.path.exists(finalFileName):
index += 1
oldSuffix = newNameSuffix
newNameSuffix = "(" + str(index) + ")"
finalFileName = finalFileName.replace(oldSuffix, newNameSuffix)
return finalFileName
def handleClient(clientSocket):
# receive file size
fileSize = int(clientSocket.recv(1024))
# print "[<==] File size received from client: %d" % fileSize
clientSocket.send("Received")
# receive file name
fileName = clientSocket.recv(1024)
# print "[<==] File name received from client: %s" % fileName
clientSocket.send("Received")
fileName = checkFileName(fileName)
file = open(fileName, 'wb')
# receive file content
print "[==>] Saving file to %s" % fileName
receivedLength = 0
while receivedLength < fileSize:
bufLen = 1024
if fileSize - receivedLength < bufLen:
bufLen = fileSize - receivedLength
buf = clientSocket.recv(bufLen)
file.write(buf)
receivedLength += len(buf)
process = int(float(receivedLength) / float(fileSize) * 100)
progressbar(process, 100)
file.close()
print "\r\n[==>] File %s saved." % fileName
clientSocket.send("Received")
while True:
client, addr = server.accept()
print "[*] Accepted connection from: %s:%d" % (addr[0], addr[1])
clientHandler = threading.Thread(target=handleClient, args=(client,))
clientHandler.start()
运行结果示例:
服务器端:
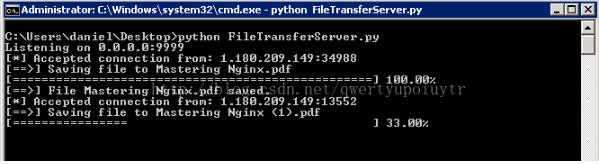
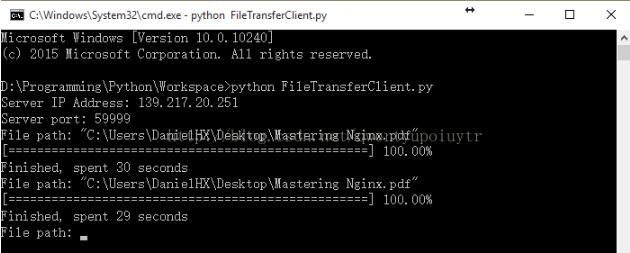
客户端(服务器端做了端口映射:59999->9999):
以上这篇python单线程文件传输的实例(C/S)就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持【听图阁-专注于Python设计】。