python实现将文件夹内的每张图片批量分割成多张
一、说在前面
需求:有一张长为960,宽为96的图片,需要将其分割成10张96*96的图片并存放在另外一个文件夹下,通过手工分割耗时且不规范,选择python写一个简单的程序完成。
二、源码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Thu Aug 23 18:19:09 2018
@author: Administrator
"""
import os
from PIL import Image
# 切割图片
def splitimage(src, rownum, colnum, dstpath):
img = Image.open(src)
w, h = img.size
if rownum <= h and colnum <= w:
print('Original image info: %sx%s, %s, %s' % (w, h, img.format, img.mode))
print('图片切割')
s = os.path.split(src)
if dstpath == '':
dstpath = s[0]
fn = s[1].split('.')
basename = fn[0]
ext = fn[-1]
num = 0
rowheight = h // rownum
colwidth = w // colnum
for r in range(rownum):
for c in range(colnum):
box = (c * colwidth, r * rowheight, (c + 1) * colwidth, (r + 1) * rowheight)
img.crop(box).save(os.path.join(dstpath, basename + '_' + str(num) + '.' + ext), ext)
num = num + 1
print('共生成 %s 张小图片。' % num)
else:
print('error')
# 创建文件夹
def mkdir(path):
# 去除首位空格
path = path.strip()
# 去除尾部 \ 符号
path = path.rstrip("\\")
# 判断路径是否存在
# 存在 True
# 不存在 False
isExists = os.path.exists(path)
# 判断结果
if not isExists:
os.makedirs(path)
print (path+' 创建成功')
return True
else:
print (path + ' 目录已存在')
return False
folder = r'C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/testresults' # 存放图片的文件夹
path = os.listdir(folder)
# print(path)
for each_bmp in path: # 批量操作
first_name, second_name = os.path.splitext(each_bmp)
each_bmp = os.path.join(folder, each_bmp)
src = each_bmp
print(src)
print(first_name)
# 定义要创建的目录
mkpath = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/results/"+ first_name
# 调用函数
mkdir(mkpath)
if os.path.isfile(src):
dstpath = mkpath
if (dstpath == '') or os.path.exists(dstpath):
row = int(1) # 切割行数
col = int(10) # 切割列数
if row > 0 and col > 0:
splitimage(src, row, col, dstpath)
else:
print('无效的')
else:
print('图片保存目录 %s 不存在!' % dstpath)
else:
print('图片文件 %s 不存在!' % src)
三、写在后面
这里定义了切割行数和列数:
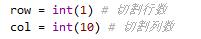
如果需要将图片更改尺寸,可以简单的使用PIL库中的resize()函数,代码如下:
from PIL import Image
for i in range(1,100):
img = Image.open("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/test_results/"+str(i)+".png")
img = img.convert("L")
img = img.resize((960,96))
img.save("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/test_results/"+str(i)+".png", "PNG")
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持【听图阁-专注于Python设计】。
