Python3.5 Pandas模块缺失值处理和层次索引实例详解
本文实例讲述了Python3.5 Pandas模块缺失值处理和层次索引。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
1、pandas缺失值处理

import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series,DataFrame
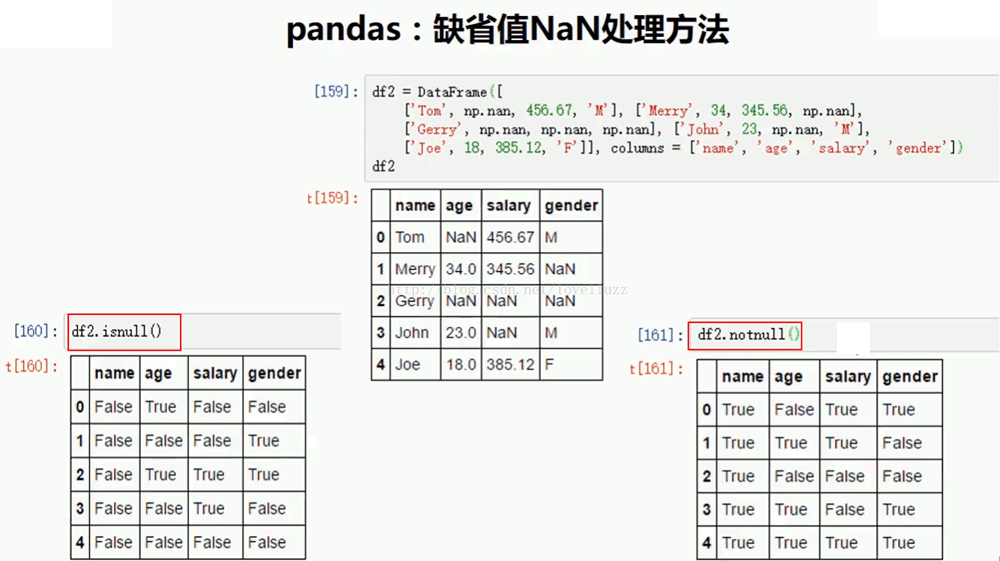
df3 = DataFrame([
["Tom",np.nan,456.67,"M"],
["Merry",34,345.56,np.nan],
[np.nan,np.nan,np.nan,np.nan],
["John",23,np.nan,"M"],
["Joe",18,385.12,"F"]
],columns = ["name","age","salary","gender"])
print(df3)
print("=======判断NaN值=======")
print(df3.isnull())
print("=======判断非NaN值=======")
print(df3.notnull())
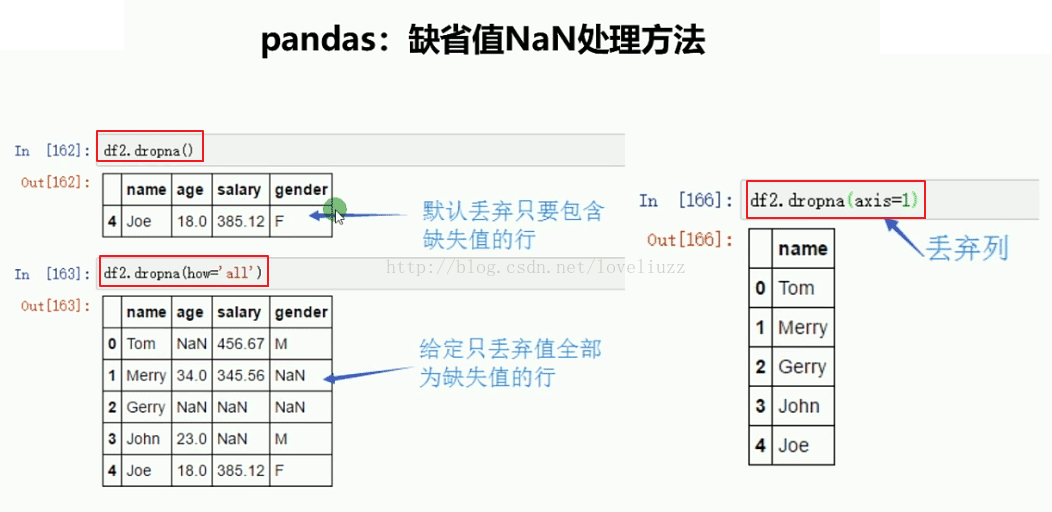
print("=======删除包含NaN值的行=======")
print(df3.dropna())
print("=======删除全部为NaN值的行=======")
print(df3.dropna(how="all"))
df3.ix[2,0] = "Gerry" #修改第2行第0列的值
print(df3)
print("=======删除包含NaN值的列=======")
print(df3.dropna(axis=1))
运行结果:
name age salary gender
0 Tom NaN 456.67 M
1 Merry 34.0 345.56 NaN
2 NaN NaN NaN NaN
3 John 23.0 NaN M
4 Joe 18.0 385.12 F
=======判断NaN值=======
name age salary gender
0 False True False False
1 False False False True
2 True True True True
3 False False True False
4 False False False False
=======判断非NaN值=======
name age salary gender
0 True False True True
1 True True True False
2 False False False False
3 True True False True
4 True True True True
=======删除包含NaN值的行=======
name age salary gender
4 Joe 18.0 385.12 F
=======删除全部为NaN值的行=======
name age salary gender
0 Tom NaN 456.67 M
1 Merry 34.0 345.56 NaN
3 John 23.0 NaN M
4 Joe 18.0 385.12 F
name age salary gender
0 Tom NaN 456.67 M
1 Merry 34.0 345.56 NaN
2 Gerry NaN NaN NaN
3 John 23.0 NaN M
4 Joe 18.0 385.12 F
=======删除包含NaN值的列=======
name
0 Tom
1 Merry
2 Gerry
3 John
4 Joe
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series,DataFrame
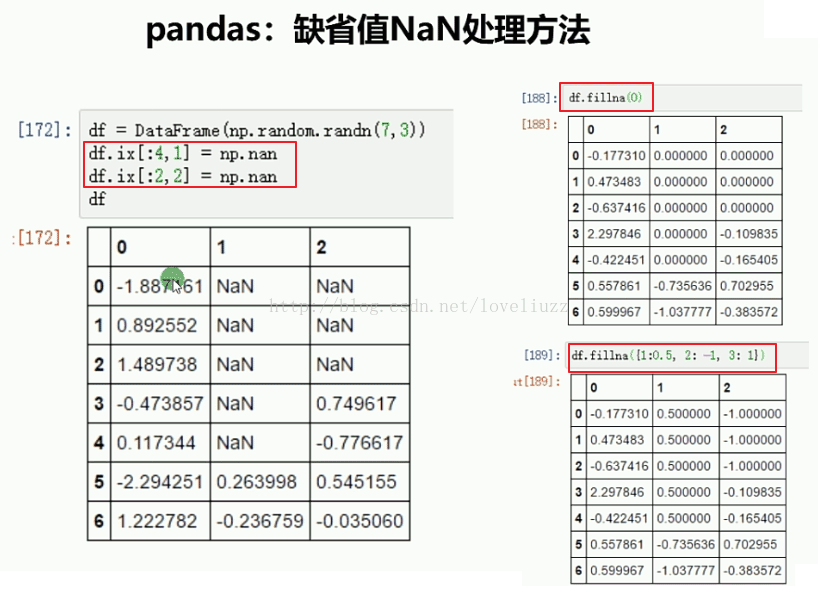
df4 = DataFrame(np.random.randn(7,3))
print(df4)
df4.ix[:4,1] = np.nan #第0至3行,第1列的数据
df4.ix[:2,2] = np.nan
print(df4)
print(df4.fillna(0)) #将缺失值用传入的指定值0替换
print(df4.fillna({1:0.5,2:-1})) #将缺失值按照指定形式填充
运行结果:
0 1 2
0 -0.737618 -0.530302 -2.716457
1 0.810339 0.063028 -0.341343
2 0.070564 0.347308 -0.121137
3 -0.501875 -1.573071 -0.816077
4 -2.159196 -0.659185 -0.885185
5 0.175086 -0.954109 -0.758657
6 0.395744 -0.875943 0.950323
0 1 2
0 -0.737618 NaN NaN
1 0.810339 NaN NaN
2 0.070564 NaN NaN
3 -0.501875 NaN -0.816077
4 -2.159196 NaN -0.885185
5 0.175086 -0.954109 -0.758657
6 0.395744 -0.875943 0.950323
0 1 2
0 -0.737618 0.000000 0.000000
1 0.810339 0.000000 0.000000
2 0.070564 0.000000 0.000000
3 -0.501875 0.000000 -0.816077
4 -2.159196 0.000000 -0.885185
5 0.175086 -0.954109 -0.758657
6 0.395744 -0.875943 0.950323
0 1 2
0 -0.737618 0.500000 -1.000000
1 0.810339 0.500000 -1.000000
2 0.070564 0.500000 -1.000000
3 -0.501875 0.500000 -0.816077
4 -2.159196 0.500000 -0.885185
5 0.175086 -0.954109 -0.758657
6 0.395744 -0.875943 0.950323
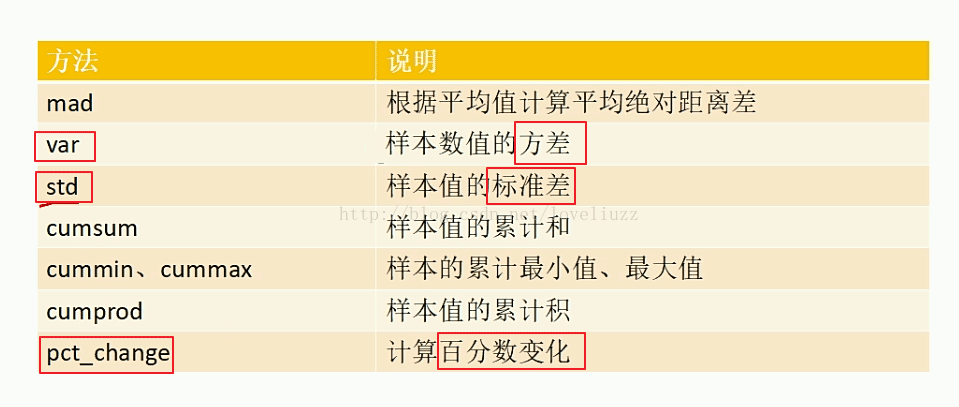
2、pandas常用数学统计方法
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series,DataFrame
#pandas常用数学统计方法
arr = np.array([
[98.5,89.5,88.5],
[98.5,85.5,88],
[70,85,60],
[80,85,82]
])
df1 = DataFrame(arr,columns=["语文","数学","英语"])
print(df1)
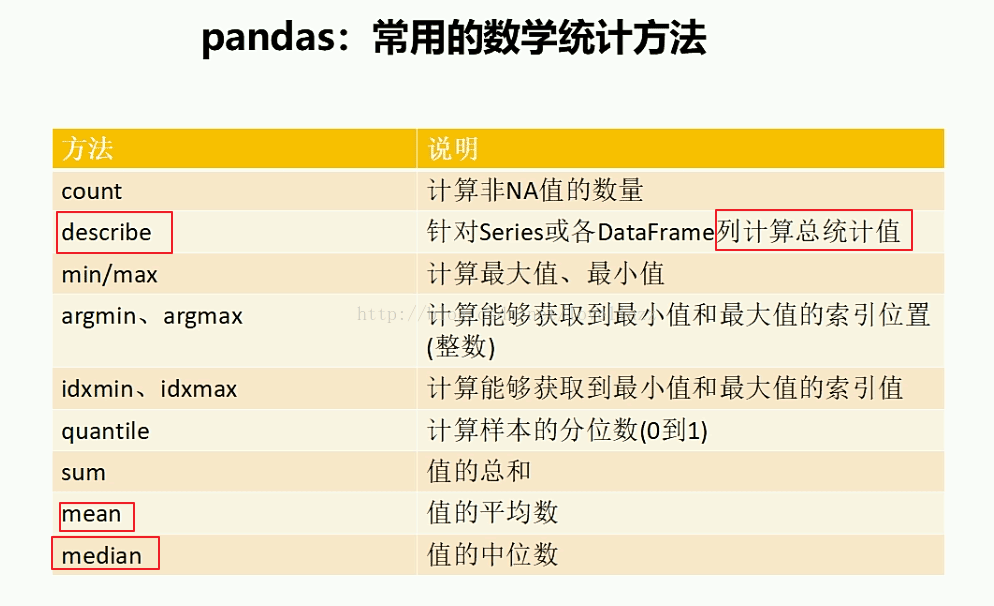
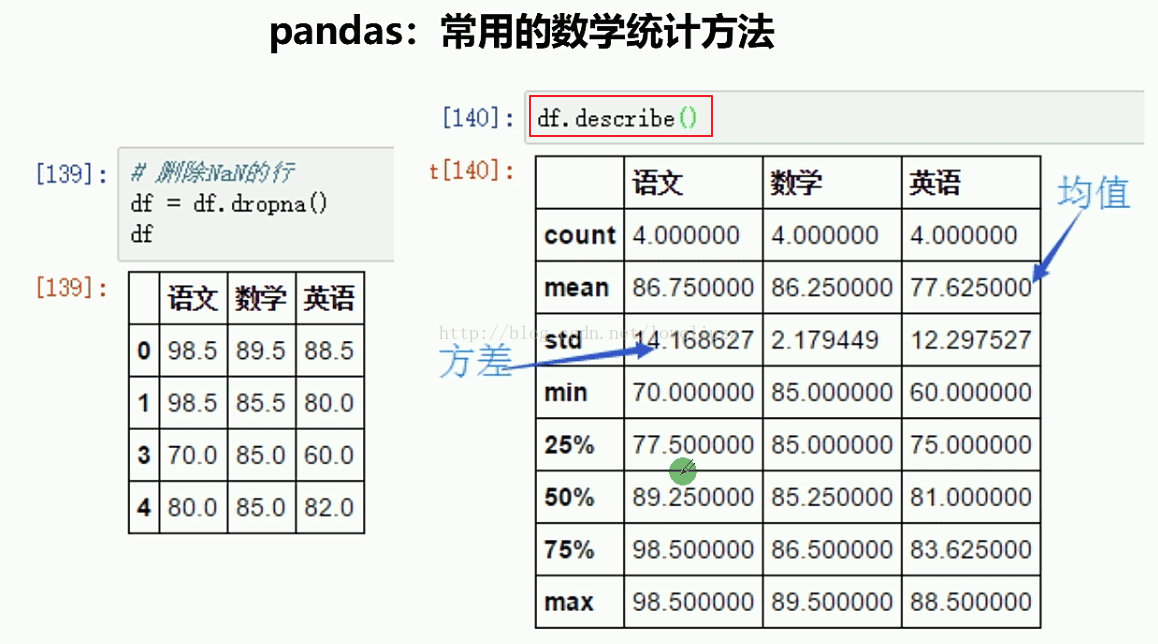
print("=======针对列计算总统计值=======")
print(df1.describe())
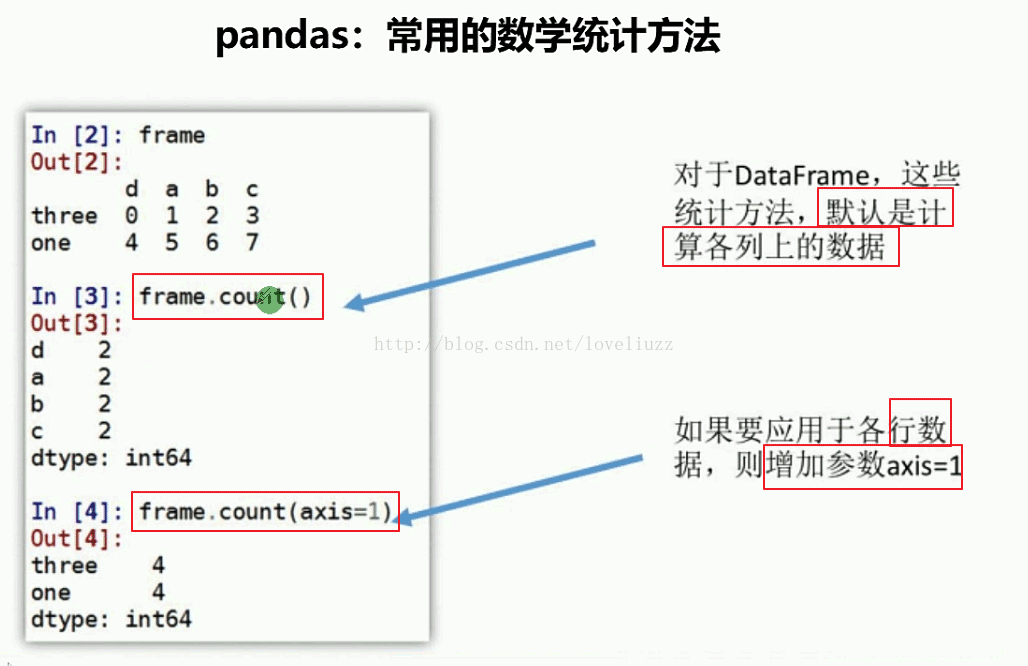
print("=======默认计算各列非NaN值个数=======")
print(df1.count())
print("=======计算各行非NaN值个数=======")
print(df1.count(axis=1))
运行结果:
语文 数学 英语
0 98.5 89.5 88.5
1 98.5 85.5 88.0
2 70.0 85.0 60.0
3 80.0 85.0 82.0
=======针对列计算总统计值=======
语文 数学 英语
count 4.000000 4.000000 4.000000
mean 86.750000 86.250000 79.625000
std 14.168627 2.179449 13.412525
min 70.000000 85.000000 60.000000
25% 77.500000 85.000000 76.500000
50% 89.250000 85.250000 85.000000
75% 98.500000 86.500000 88.125000
max 98.500000 89.500000 88.500000
=======默认计算各列非NaN值个数=======
语文 4
数学 4
英语 4
dtype: int64
=======计算各行非NaN值个数=======
0 3
1 3
2 3
3 3
dtype: int64

import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series,DataFrame、
#2.pandas相关系数与协方差
df2 = DataFrame({
"GDP":[12,23,34,45,56],
"air_temperature":[23,25,26,27,30],
"year":["2001","2002","2003","2004","2005"]
})
print(df2)
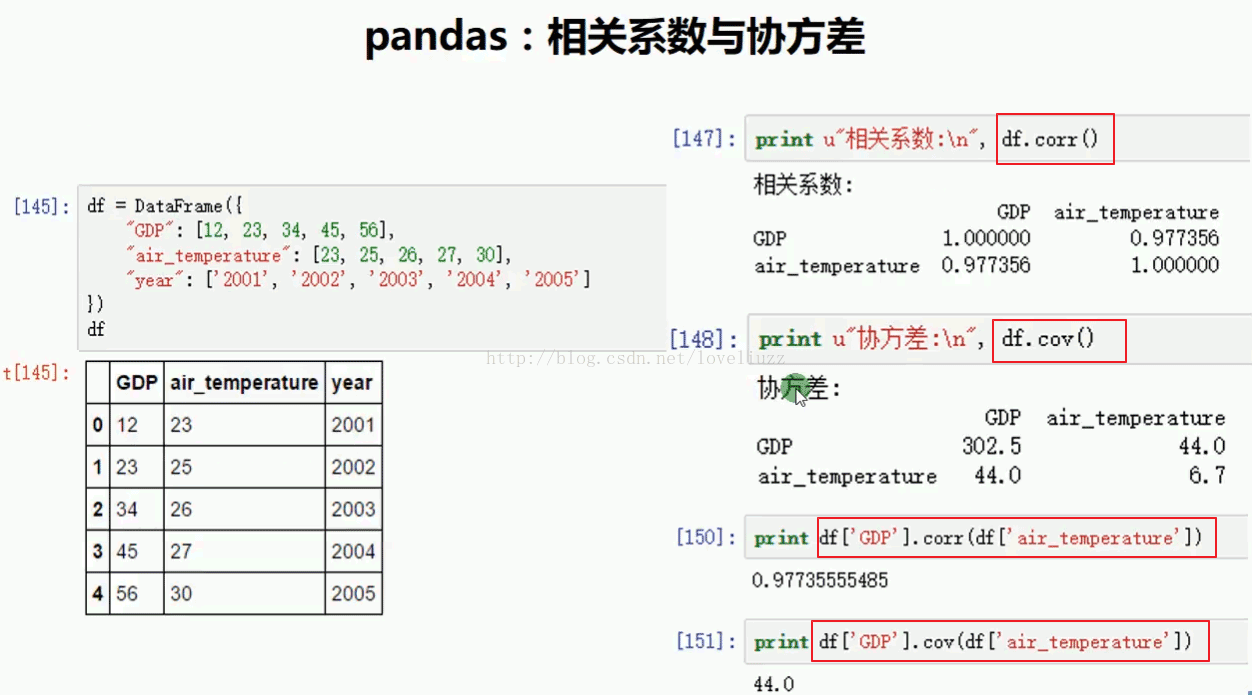
print("=========相关系数========")
print(df2.corr())
print("=========协方差========")
print(df2.cov())
print("=========两个量之间的相关系数========")
print(df2["GDP"].corr(df2["air_temperature"]))
print("=========两个量之间协方差========")
print(df2["GDP"].cov(df2["air_temperature"]))
运行结果:
GDP air_temperature year
0 12 23 2001
1 23 25 2002
2 34 26 2003
3 45 27 2004
4 56 30 2005
=========相关系数========
GDP air_temperature
GDP 1.000000 0.977356
air_temperature 0.977356 1.000000
=========协方差========
GDP air_temperature
GDP 302.5 44.0
air_temperature 44.0 6.7
=========两个量之间的相关系数========
0.97735555485
=========两个量之间协方差========
44.0

import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series,DataFrame
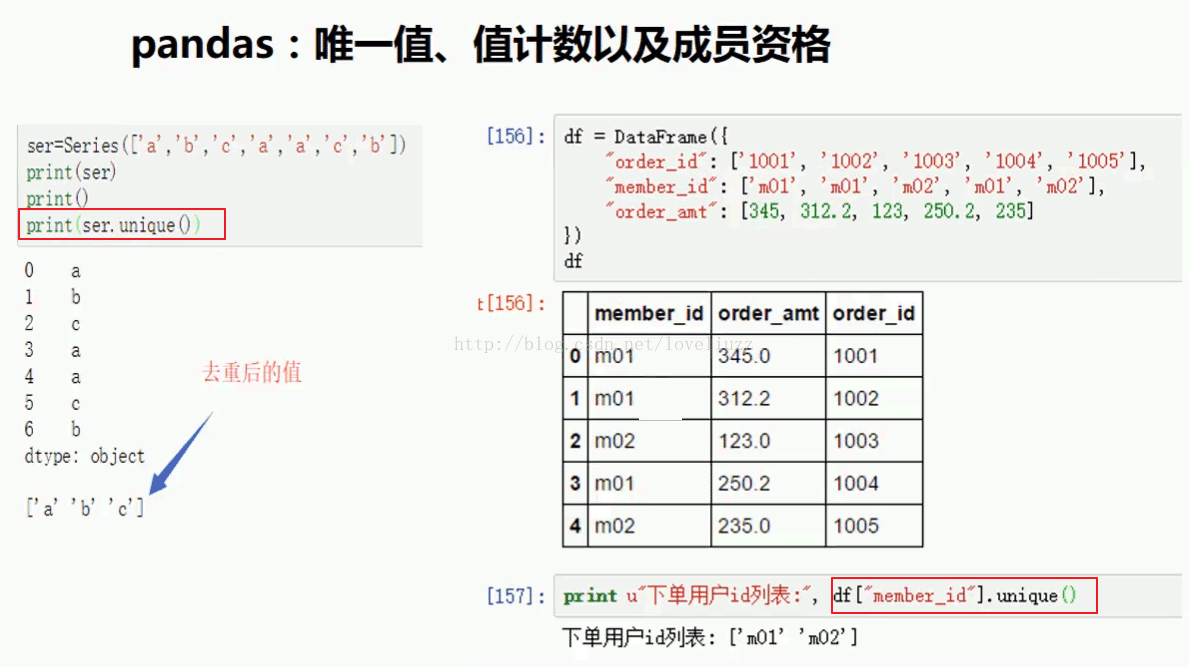
#3.pandas唯一值、值计数及成员资格
df3 = DataFrame({
"order_id":["1001","1002","1003","1004","1005"],
"member_id":["m01","m01","m02","m01","m02",],
"order_amt":[345,312.2,123,250.2,235]
})
print(df3)
print("=========去重后的数组=========")
print(df3["member_id"].unique())
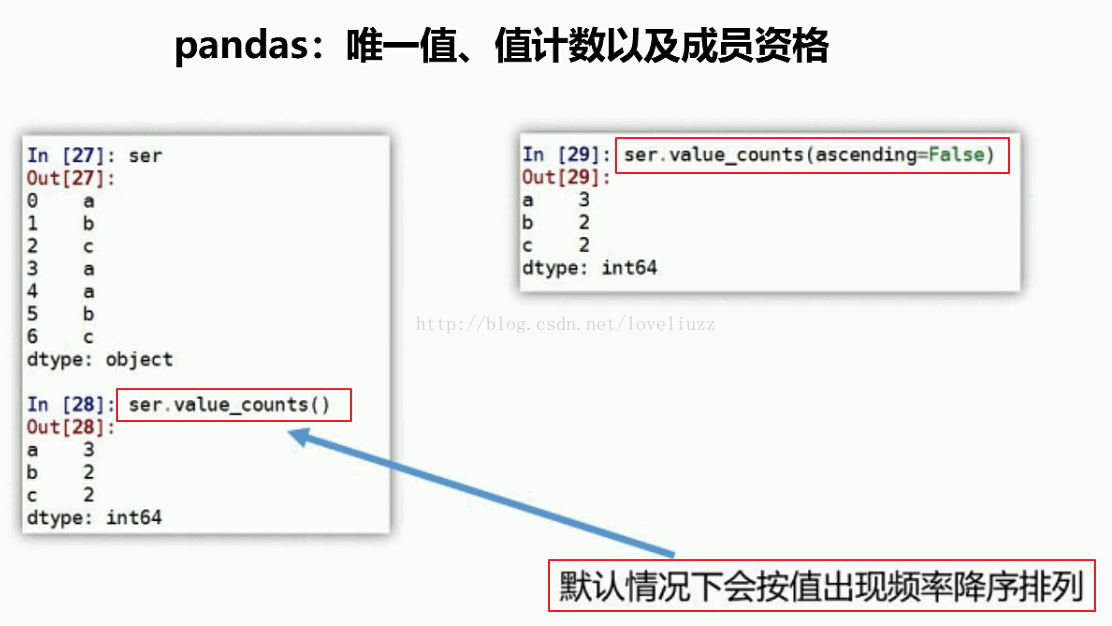
print("=========值出现的频率=========")
print(df3["member_id"].value_counts())
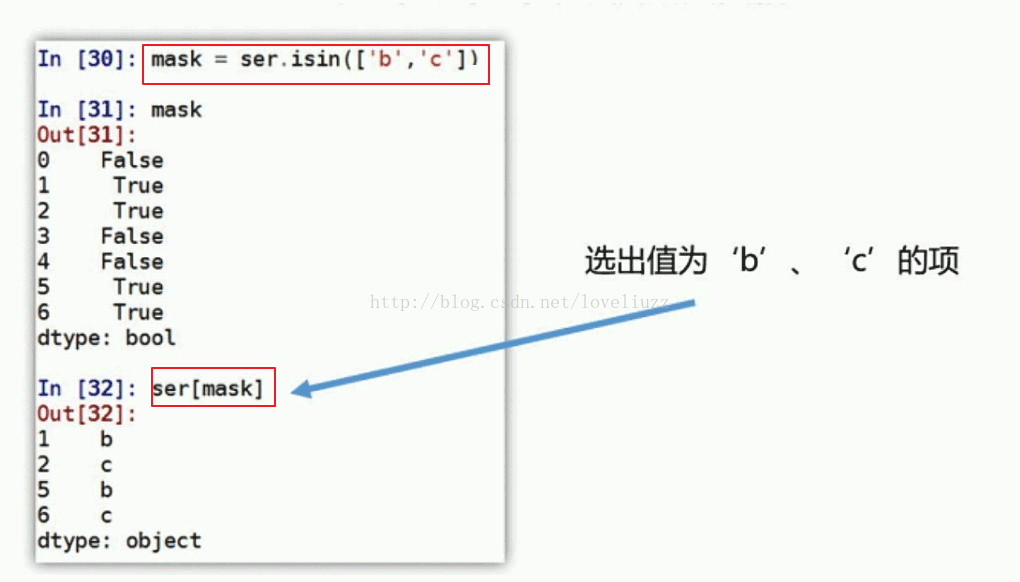
print("=========成员资格=========")
df3 = df3["member_id"]
mask = df3.isin(["m01"])
print(mask)
print(df3[mask])
运行结果:
member_id order_amt order_id
0 m01 345.0 1001
1 m01 312.2 1002
2 m02 123.0 1003
3 m01 250.2 1004
4 m02 235.0 1005
=========去重后的数组=========
['m01' 'm02']
=========值出现的频率=========
m01 3
m02 2
Name: member_id, dtype: int64
=========成员资格=========
0 True
1 True
2 False
3 True
4 False
Name: member_id, dtype: bool
0 m01
1 m01
3 m01
Name: member_id, dtype: object
3、pandas层次索引

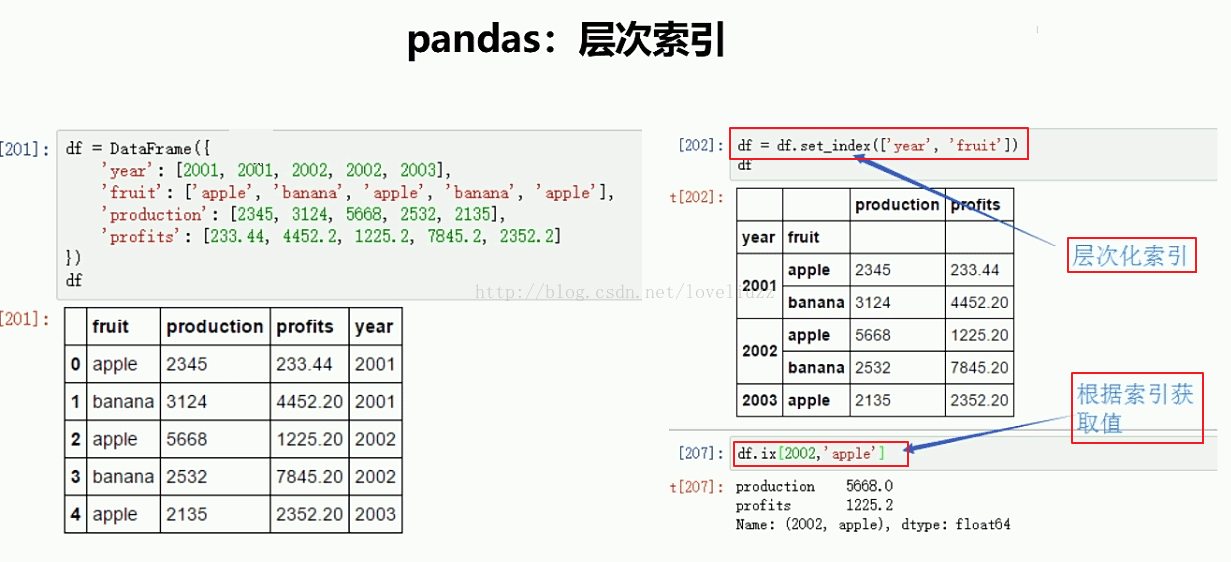
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series,DataFrame
#3.pandas层次索引
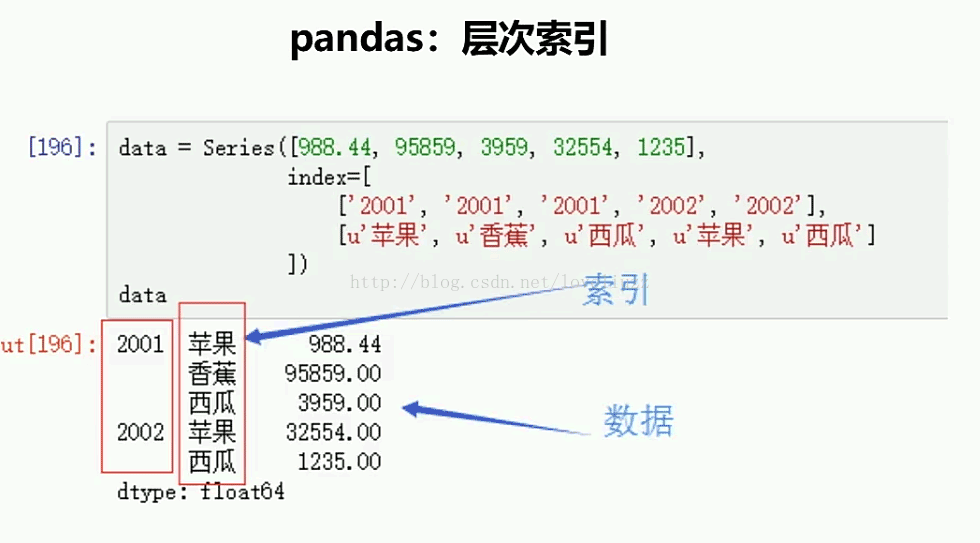
data = Series([998.4,6455,5432,9765,5432],
index=[["2001","2001","2001","2002","2002"],
["苹果","香蕉","西瓜","苹果","西瓜"]]
)
print(data)
df4 = DataFrame({
"year":[2001,2001,2002,2002,2003],
"fruit":["apple","banana","apple","banana","apple"],
"production":[2345,5632,3245,6432,4532],
"profits":[245.6,432.7,534.1,354,467.8]
})
print(df4)
print("=======层次化索引=======")
df4 = df4.set_index(["year","fruit"])
print(df4)
print("=======依照索引取值=======")
print(df4.ix[2002,"apple"])
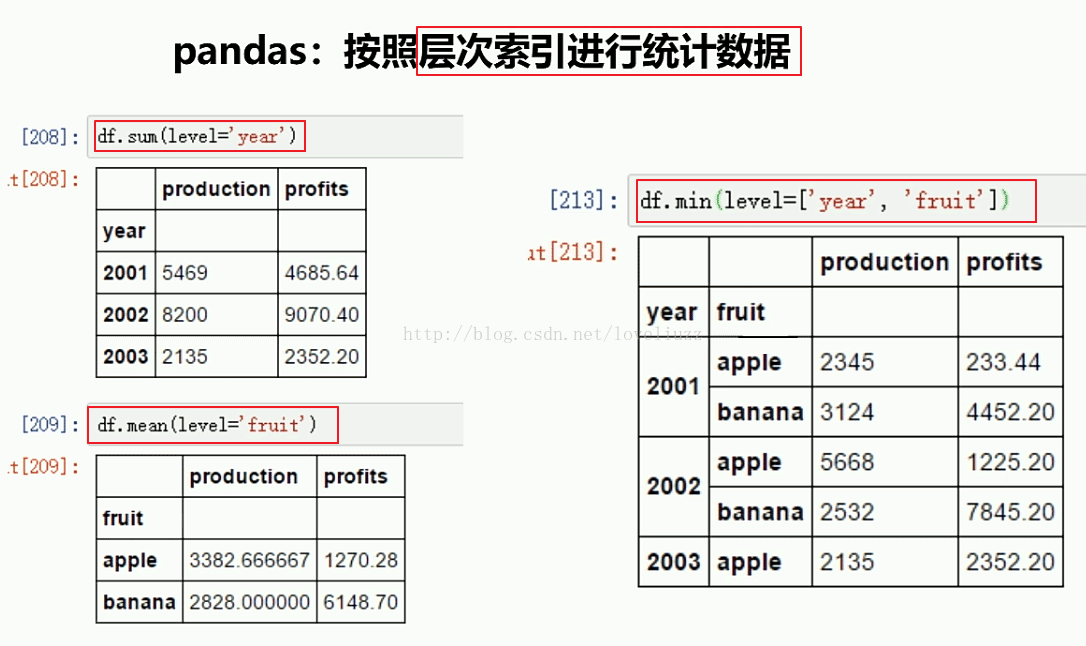
print("=======依照层次化索引统计数据=======")
print(df4.sum(level="year"))
print(df4.mean(level="fruit"))
print(df4.min(level=["year","fruit"]))
运行结果:
2001 苹果 998.4
香蕉 6455.0
西瓜 5432.0
2002 苹果 9765.0
西瓜 5432.0
dtype: float64
fruit production profits year
0 apple 2345 245.6 2001
1 banana 5632 432.7 2001
2 apple 3245 534.1 2002
3 banana 6432 354.0 2002
4 apple 4532 467.8 2003
=======层次化索引=======
production profits
year fruit
2001 apple 2345 245.6
banana 5632 432.7
2002 apple 3245 534.1
banana 6432 354.0
2003 apple 4532 467.8
=======依照索引取值=======
production 3245.0
profits 534.1
Name: (2002, apple), dtype: float64
=======依照层次化索引统计数据=======
production profits
year
2001 7977 678.3
2002 9677 888.1
2003 4532 467.8
production profits
fruit
apple 3374 415.833333
banana 6032 393.350000
production profits
year fruit
2001 apple 2345 245.6
banana 5632 432.7
2002 apple 3245 534.1
banana 6432 354.0
2003 apple 4532 467.8
更多关于Python相关内容感兴趣的读者可查看本站专题:《Python数学运算技巧总结》、《Python数据结构与算法教程》、《Python函数使用技巧总结》、《Python字符串操作技巧汇总》、《Python入门与进阶经典教程》及《Python文件与目录操作技巧汇总》
希望本文所述对大家Python程序设计有所帮助。
